History of AI: Technologies, Companies, and Products
1950s
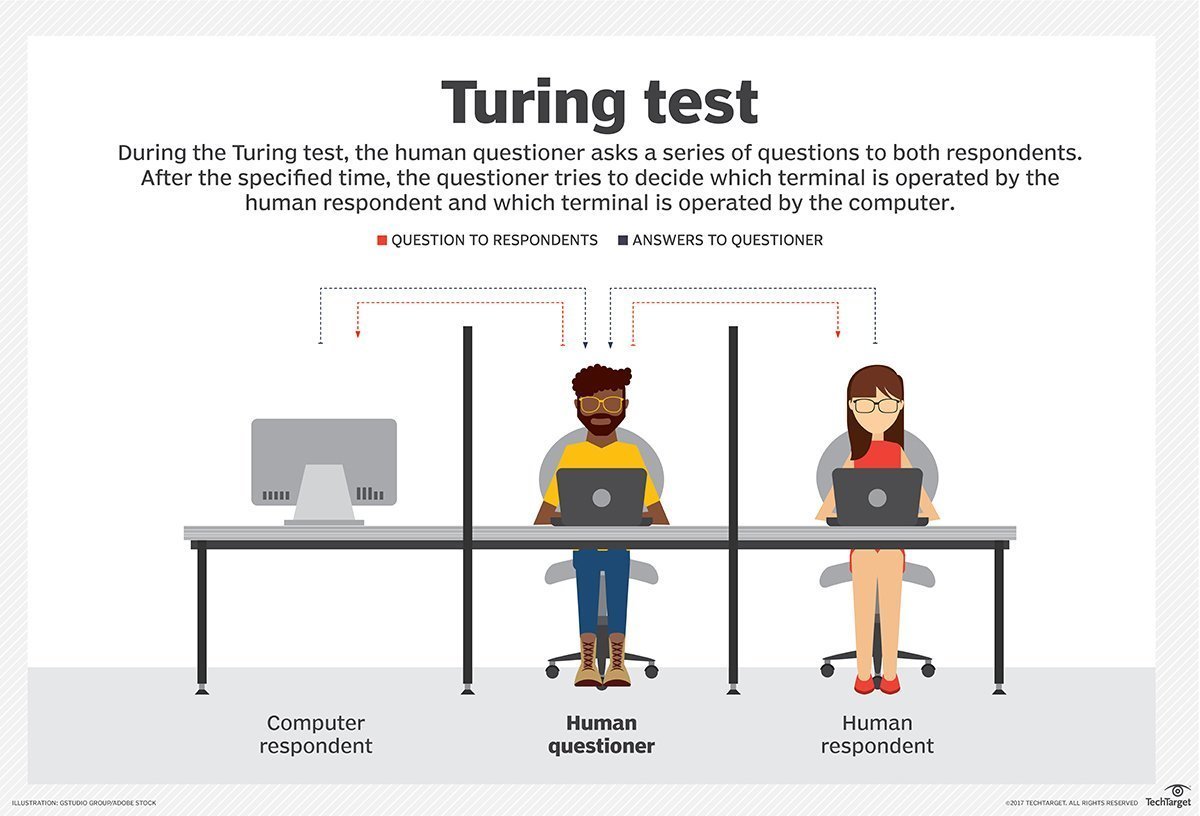
- Turing Test: In 1950, Alan Turing proposed the Turing Test to determine whether a machine can exhibit intelligent behavior.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) term: In 1956, John McCarthy coined the term “artificial intelligence” at the Dartmouth conference, marking the beginning of AI as a research field.
1960s
-
Early AI research: In the 1960s, early AI research focused on developing problem-solving techniques, such as search algorithms, symbolic manipulation, and theorem-proving.
-
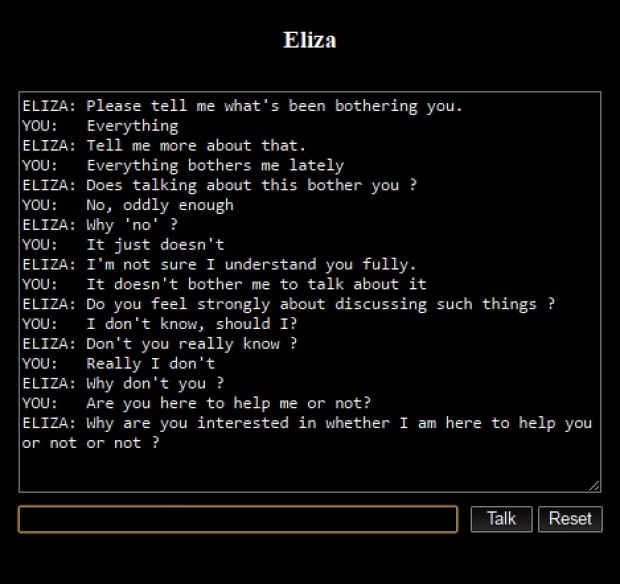
ELIZA: Developed by Joseph Weizenbaum in 1964, ELIZA was an early natural language processing computer program that could simulate conversation.
- SHRDLU: Developed by Terry Winograd in 1968-1970, SHRDLU was a computer program that could understand and respond to queries about a virtual world of blocks.
1970s
-
Expert systems: The 1970s saw the development of expert systems, which used knowledge-based approaches to solve complex problems. MYCIN, developed at Stanford University, was one of the earliest expert systems for diagnosing infectious diseases.
-
Speech recognition: In the late 1970s, early speech recognition systems, such as the Harpy program at Carnegie Mellon University, were developed.
1980s
-
Machine learning: The 1980s witnessed the rise of machine learning techniques, such as decision trees and neural networks, for building intelligent systems.
-
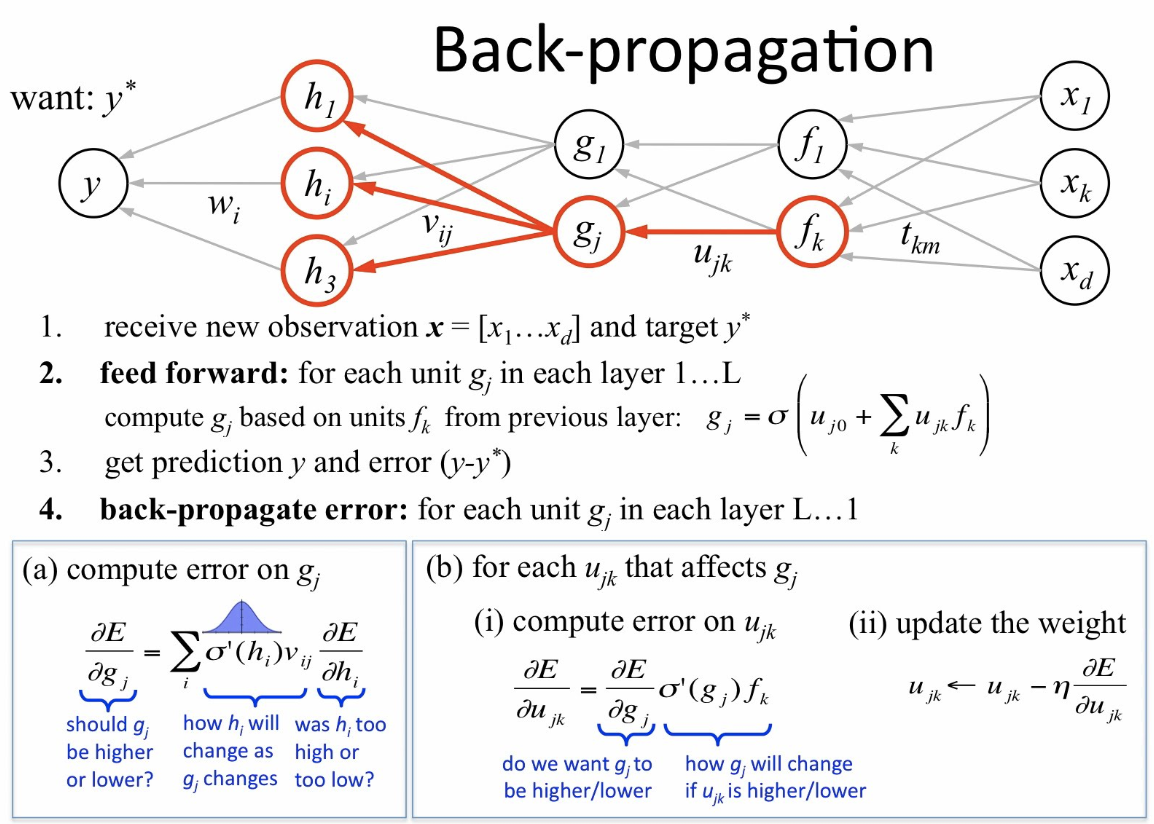
Backpropagation: In 1986, Geoffrey Hinton, David Rumelhart, and Ronald Williams introduced the backpropagation algorithm, which significantly improved the training of neural networks.
- Autonomous vehicles: In the late 1980s, Carnegie Mellon University’s Navlab project and the German Aerospace Center’s EUREKA Prometheus Project started developing autonomous vehicle technology.
1990s
-
Deep Blue: In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue chess computer defeated world champion Garry Kasparov, showcasing the potential of AI. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KF6sLCeBj0s
-
Reinforcement learning: During the 1990s, reinforcement learning techniques, such as Q-learning, were developed for training agents to make decisions based on rewards and penalties.
2000s
-
Natural language processing: In the 2000s, natural language processing techniques, such as sentiment analysis and machine translation, gained prominence.
-
Siri: In 2010, Apple acquired Siri, a virtual assistant, and integrated it into the iPhone, popularizing voice-activated AI assistants.
2010s
-
Deep learning: The 2010s saw the rise of deep learning, which led to significant advancements in image and speech recognition.
-
ImageNet competition: From 2010 to 2017, the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge accelerated the development of AI for image recognition, with deep learning techniques dominating the competition.
-
AlphaGo: In 2016, DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated the world champion Go player Lee Sedol, showcasing the potential of deep learning and reinforcement learning in AI.

-
Virtual assistants: In the 2010s, virtual assistants like Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and Microsoft Cortana became popular consumer products.
-
Self-driving cars: Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Cruise Automation made significant advancements in autonomous vehicle technology during this decade.
-
GPT-2 and GPT-3: OpenAI released its second-generation language model, GPT-2, in 2019, which could generate highly convincing text. In 2020